Func in C#:
We have learned in the previous section, that a delegates can be defined as shown below.
Example: C# Delegate
public delegate int SomeOperation(int i, int j);
class Program
{
static int Sum(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SomeOperation add = Sum;
int result = add(10, 10);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
Output:
20
C# 3.0 includes built-in generic delegate types Func and Action, so that you don't need to define custom delegates as above.
Func is a generic delegate included in the System namespace. It has zero or more input parameters and one out parameter. The last parameter is considered as an out parameter.
For example, a Func delegate that takes one input parameter and one out parameter is defined in the System namespace as below:
Func in C#:
namespace System
{
public delegate TResult Func<in T, out TResult>(T arg);
}
The last parameter in the angle brackets <> is considered as the return type and remaining parameters are considered as input parameter types as shown in the following figure.
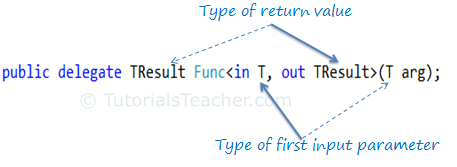 Func delegate
Func delegate
A Func delegate with two input parameters and one out parameters will be represent as below.
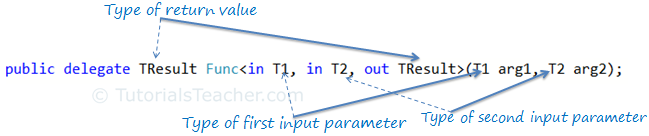 Func delegate
Func delegate
The following Func type delegate is the same as the above SomeOperation delegate, where it takes two input parameters of int type and returns a value of int type:
You can assign any method to the above func delegate that takes two int parameters and returns an int value. Now, you can take Func delegate instead of someOperation delegate in the first example.
Example: Func
class Program
{
static int Sum(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Func<int,int, int> add = Sum;
int result = add(10, 10);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
Output:
20
A Func delegate type can include 0 to 16 input parameters of different types. However, it must include one out parameter for result.
For example, the following func delegate doesn't have any input parameter, it includes only a out parameter.
Example: Func with zero input parameter
Func<int> getRandomNumber;
Func with an Anonymous method:
You can assign an anonymous method to the Func delegate by using the delegate keyword.
Example: Func with anonymous method
Func<int> getRandomNumber = delegate()
{
Random rnd = new Random();
return rnd.Next(1, 100);
};
Func with lambda expression:
A Func delegate can also be used with a lambda expression, as shown below:
Example: Func with lambda expression
Func<int> getRandomNumber = () => new Random().Next(1, 100);
//Or
Func<int, int, int> Sum = (x, y) => x + y;
Points to Remember :
- Func is built-in delegate type.
- Func delegate type must return a value.
- Func delegate type can have zero to 16 input parameters.
- Func delegate type can be used with an anonymous method or lambda expression.